Copy the shapefile into a new empty folder. Only take the SHP, SHX, and DBF with you. Leave all other files behind, and yes that includes the prj. (Windows): right-click the SHX file and select 'Properties' to open the file properties. On the 'General' tab take a look at the EXACT file size of this SHX file down to the byte. Winsock Repair 1.0.5.1052 is a small, though discontinued tool that can help resolve networking issues on Windows systems by repairing and/or resetting the Windows socks. The main interface of this application is very easy-to-understand, containing only a few buttons to get the task complet. This tool troubleshoots common issues with the setup of Microsoft.NET Framework or with updates to Microsoft.NET Framework setup installation. Additionally, this tool tries to resolve these issues by applying known fixes or by repairing the installed product.
Shapefile Repair Tool 1.0 Pro
The instructions below describe several options to help in salvaging a corrupt shapefile. Common causes of corruptions are a computer crash while saving edits; adding illegal geometry, for example, bow ties; or modifying the attribute table with other software, for example, Microsoft Excel. If the steps listed here do not salvage the shapefile, you will have to revert to the backup.
Shapefile Repair Tool 1.0 Free
Options used to salvage a shapefile
Verify a backup of the data was made before attempting any of these options:
- Use the Check Geometry tool. Problems with the data are reported while the tool is executing or in the output table. View the output table after execution. An empty table indicates that the tool found no bad geometry. If bad geometry is reported, use the Repair Geometry tool.
- Try using the Repair Geometry tool.
- Attempt to copy the data to a geodatabase. Afterward, also try copying it back to a new shapefile.
- Try selecting all or a subset of the features and export the selected features to a new shapefile or feature class.
- If the data is on a network drive, copy it to a local drive. If the data is on a local drive, try copying it to the root of the primary drive, for example, C:.
- Check for illegal field names in the attribute table. Field names can only have 10 characters. Field names must start with a letter. Field names must not contain any spaces or special characters, except for the underscore character.
- File names must not contain any special characters, except for the underscore character. Generally speaking, spaces in shapefile names work in ArcGIS for Desktop; however, for testing purposes, rename the shapefile so it has no spaces.
- Remove all index (spatial, attribute, and geocoding) and metadata files in Windows Explorer. That is, remove all files except .shp, .dbf, and .shx. Verify that a copy of each of these files has been made before removing them.
- Try opening the shapefile on another computer.
- Try opening the shapefile in another software application—preferably ArcView GIS 3.x.
- Try bringing the data into another feature class either by using the simple data loader or by copying and pasting in an edit session.
- If the data is still not repaired, and the first two suggestions above reported the feature IDs of the bad records, try manually removing them in an editing session.
- Try bringing the .dbf part of the shapefile into Microsoft Excel and resaving it as a dBASE 4 file. Do not make any other changes to the file.
- Try making a field calculation in ArcGIS for Desktop or ArcView GIS 3.x using the field calculator. The field calculator may stop on the corrupt record.
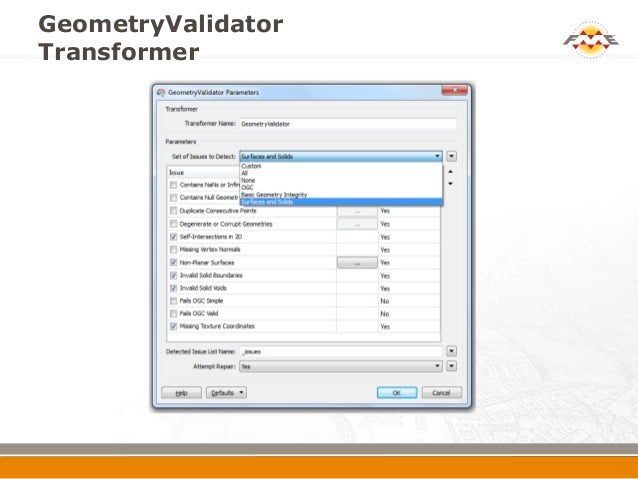
Related Topics
The Shapefile Fixer has been developed with the aim to get a “cleaned” spatial data from most common geometry errors. I focus my forces particularly on those data saved in ShapeFile format because is the most common geometry file format.
The software reads a set of shapefiles from an input folder and writes the result to an output folder. The user can decide whether to apply the geometric errors fixing process and / or the coordinates rounding process.
The fixing process eliminates geometric errors that may originate from the draw / digitization of data and / or deriver by a data post processing. The most common errors are those relating to duplicate consecutive vertices, self- overlapping lines or polygons with self-intersection / self-tangency.
The process of coordinates rounding aims to eliminate resolution errors, as a matter of fact sometimes happens that in some systems can be detected some micro-overlapping and / or micro-gap not founded in other systems. This behavior is a result of the evaluation with algorithms based on a different tolerance implementation. The coordinates rounding process aims to eliminate these problems by rounding all coordinates of all geometries present in the shapefile.

License type: CC BY-ND
Available languages software and manuals: English, Italian
Supported operating systems:
Development state: Released
Version: 1.0 – february 2014
Do you use my softwares and do you think that they can be useful? Send me an e-mail because I want to create a section called “Who uses my softwares”. Thanks